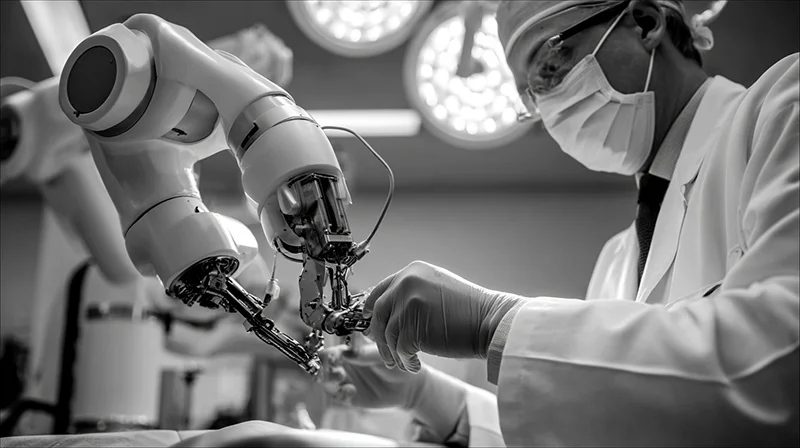
The industry structure is crucial
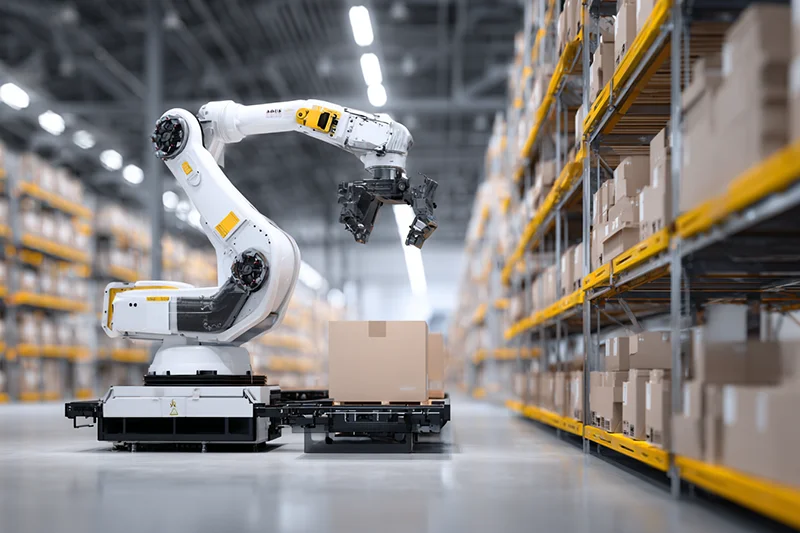
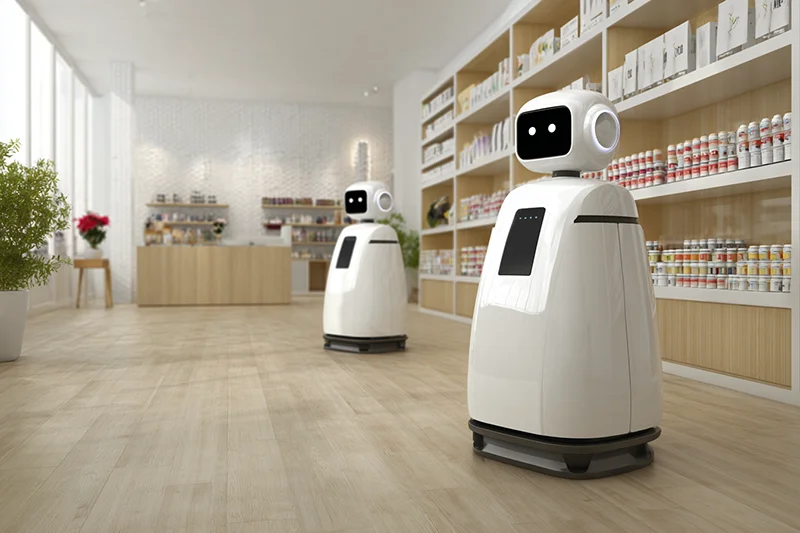
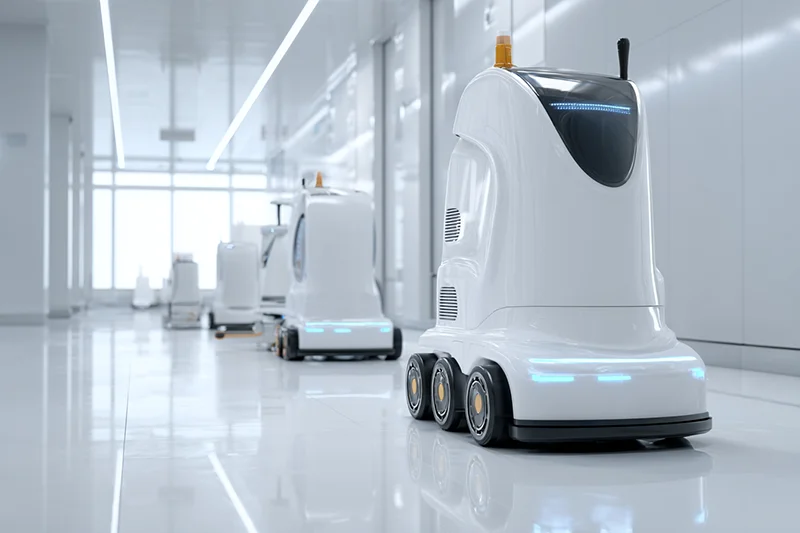
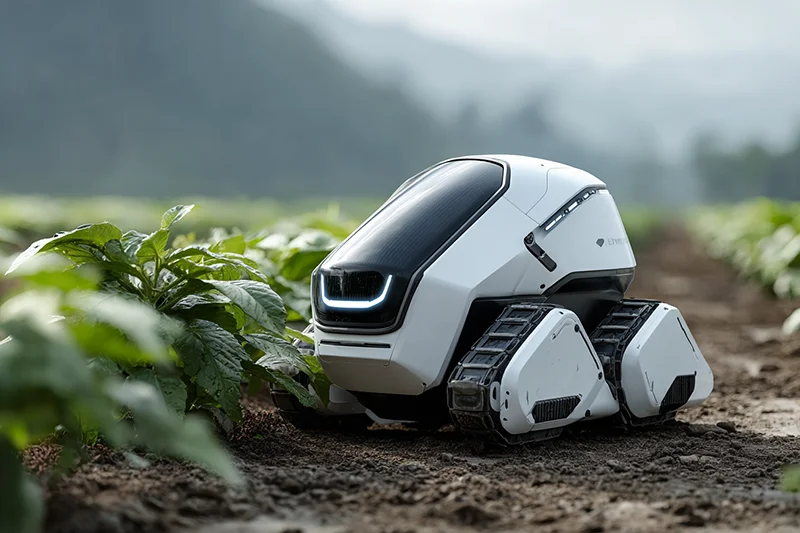
Service robotics is defined less by technology than by context of use. Unlike industrial automation, service robots are deployed across heterogeneous environments with distinct operational constraints, safety requirements, interaction patterns and economic drivers.
For this reason, international reporting applies application-based classification to ensure statistical comparability over time and across regions. The reference framework for this classification is defined by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) ↗ in its World Robotics – Service Robots methodology.
The IFR framework groups service robots by reported application classes for unit-based market analysis. These classes serve statistical purposes and are designed for longitudinal consistency rather than editorial or operational modeling.
This page follows the IFR classification as its quantitative reference, while applying an operational sector structure for editorial clarity. Sectors are therefore grouped by shared deployment environments, functional demands and governance conditions, even where IFR reporting categories differ in granularity.